Head of the laboratory: Prof. dr Ranko Antunović
Contact: 057/340-847, ext. 102
E-mail: ranko.antunovic@ues.rs.ba
Laboratory for applied mechanics and mechanical constructions
Laboratory equipment and activities:
1. Development of new measuring devices, monitoring and diagnostic systems
Modular measuring and acquisition system
LabView Full Development System software package
Test bench for dynamic tests

2. Vibrodiagnostic tests and analyzes
Modular portable vibration analyzer CMXA 75
Dual channel analyzer

3. Noise measurement and analysisе
Environmental protection (urban noise monitoring)
Health and safety (noise monitoring in plants and workplaces)
Acoustics of buildings
Industry

4. Numerical analysis of constructions and measurement of residual stresses of complex systems
DynaLog Strain Meter

5. Thermovision
Temperature range from -20 to 1500°C
FLIR Е4:
Sensitivity 0.15°C
Field of view 45°x34°
SKF TKTI 31:
Sensitivity 0.06°C
Shooting up to 5 temperatures with special emission at the same time
Audio recording


6. Program balance machine
CMXA balancer

7. Force measurement
AXIS FB10K
Range 10 kN

8. 3D scanner
NextEngine
3600 rotating table
Output formats: STL, OBJ, VRML, XYZ, PLY

9. Material hardness testing
HARTIP 1000
Hardness measurement by Leeb
Scales: HL / HRC / HRB / HB / HV / HS
Operating temperature from -10 to + 45°C

10. Trainings and seminars

Our work is in line with the relevant regulations, standards and recommendations expressed through the use of appropriate ISO, EN and BAS standards and recommendations.
Activities of the Laboratory for applied mechanics and mechanical constructions in the field of constructions
- Improving the process of product development and construction;
- Models, basic principles and methods in RP;
- Development and selection of methods for: goal planning; goal analysis: problem structuring; searching for alternative solutions; determining the working characteristics of the product; making decisions; ensuring the achievement of the goal;
- Modeling of technical systems in the field of function, physical effects and shapes;
- Rules, principles as well as the place and role of design in product development;
- Calculation and structural analysis of constructions for operating conditions;
- Structuring problems in RP;
- Development and construction of variant products;
- Environmental aspects in product development;
- Methodological approach to product development from the aspect of technology;
- Visualization and interaction in product development;
- Product Life Cycle (PLM) and information systems;
- Knowledge system life cycle and knowledge systems software packages;
- Methods of modeling and optimization of product development processes;
- Innovation and technology management in RP;
- Organization of learning as a focus of knowledge management;
- Human resource management in the product development process;
- Knowledge transfer and efficient use of available knowledge. Team work. Evaluation of team participants’ competencies;
- Management of variant solutions and complexity;
- Management of innovation cooperative projects;
- Development and application of decision making methods in RP;
- Apply methods to ensure goal achievement;
- Development and construction of power transmissions (reducers and multipliers – gear, worm, chain, belt, friction, planetary transmissions, variators, gearboxes, combined transmissions);
- Power transmission reliability calculation;
- Testing and diagnostics of machine systems and constructions;
- Development and application of software for construction;
- Cooperation with individual working organizations in terms of forming joint research and development teams;
- Cooperation with individual work organizations in the field of research and development of machines for various purposes according to industry requirements;
- Cooperation with scientific research centers in the world in terms of developing joint EU projects (FP7, DAAD, Tempus, etc.);
- Cooperation with scientific research centers in the world in terms of global product development;
- Initiating the development of the economic system with state institutions and local authorities in accordance with world standards for the development of quality, market-competitive products;
- Proposing and developing conceptual solutions for the introduction of global standards for sustainable development for existing and newly formed economic and service entities in their business system;
- Giving recommendations for new methods in organizing business, to help companies focus on the development and production of quality, market-competitive products, in order to survive in the market;
- Organizing CAD / CAE seminars for users of application software in the field of modeling, construction documentation, simulation, application of finite element methods in the analysis of stress-strain state of constructions (Solid Works, INVENTOR, Solid Edge, CATIA, Pro / ENGINEER, AutoCAD, Ansys, NASTRAN, PATRAN , …);
- Development and definition of technical diagnostic procedures in the process of maintenance of machine plants, gearboxes, railway vehicles;
- Management of innovative product development projects, in national and international frameworks;
- Innovation management, knowledge transfer;
- Organizing educational activities (trainings, courses, trainings, seminars, conferences) for students of other higher education institutions and engineers from practice, in the premises of the center or on site (in companies or companies).
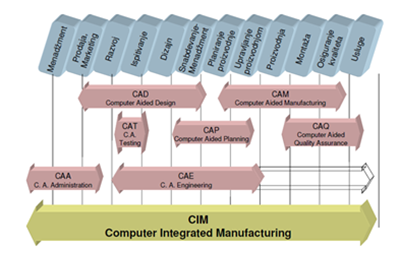
Figure 1. Scope of CAD, CAM, CAP, CAE, CIM, CAA and CAT systems
Some examples of the development of innovative products, as a result of student work, using existing knowledge in the field of mechanical construction and integrated product development follow.
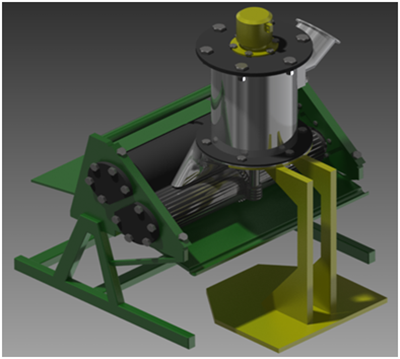
Figure 2. 3D view of the machine for simultaneous cutting and squeezing of apples
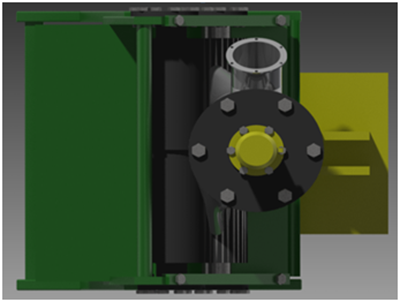
Figure 3. 3D view of the machine for simultaneous cutting and squeezing of apples (top view)
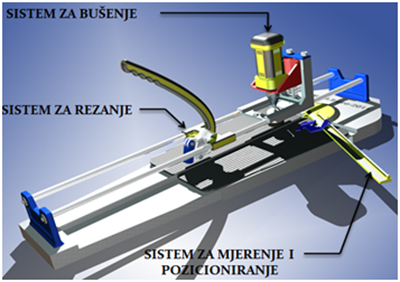
Figure 4. Machine for cutting and drilling ceramic tiles
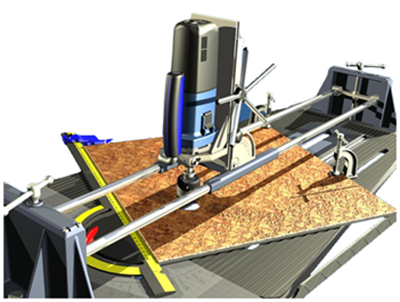
Figure 5. 3D model of a tool for drilling ceramic tiles
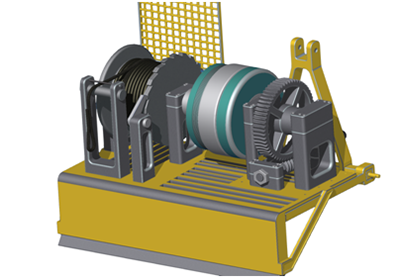
Figure 6. 3D model of a log extraction machine